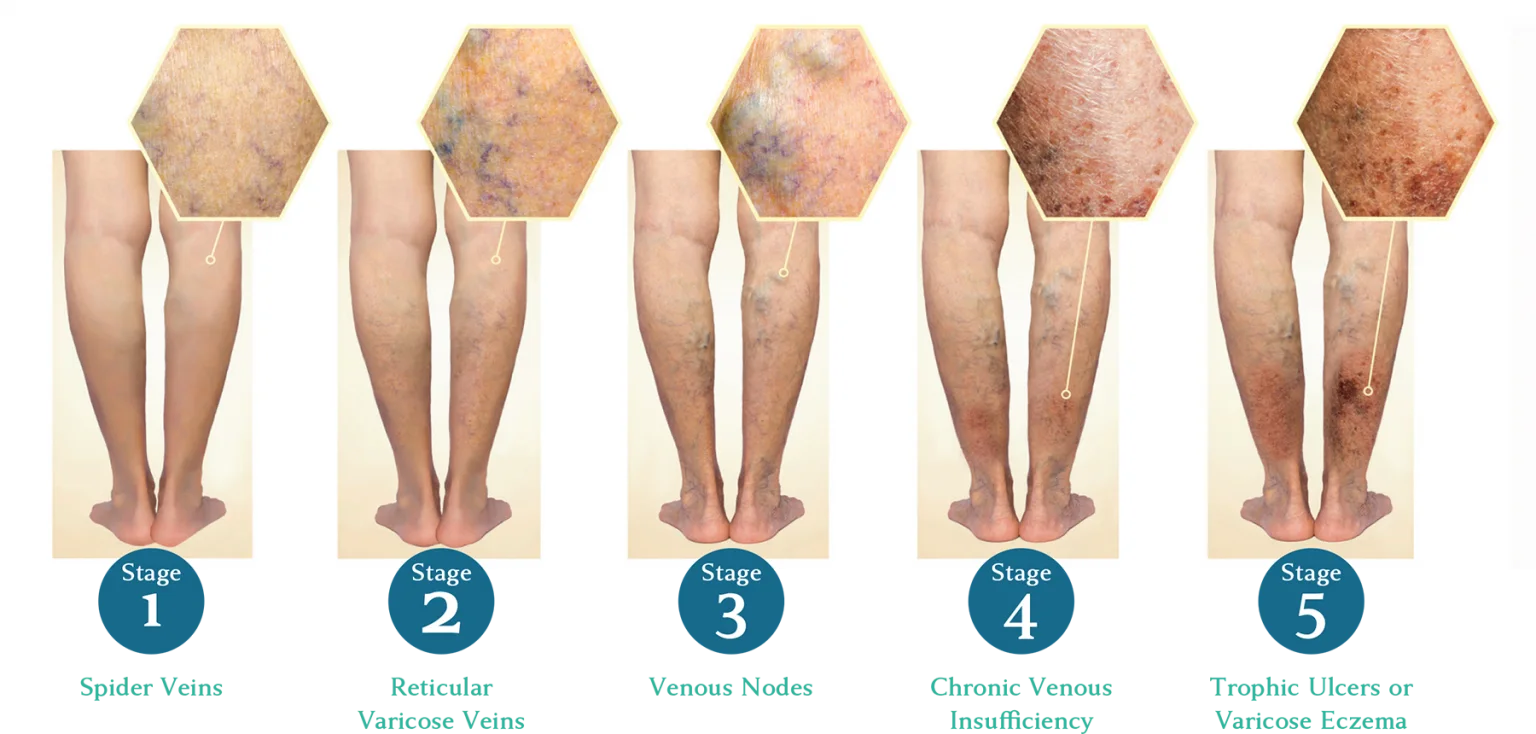
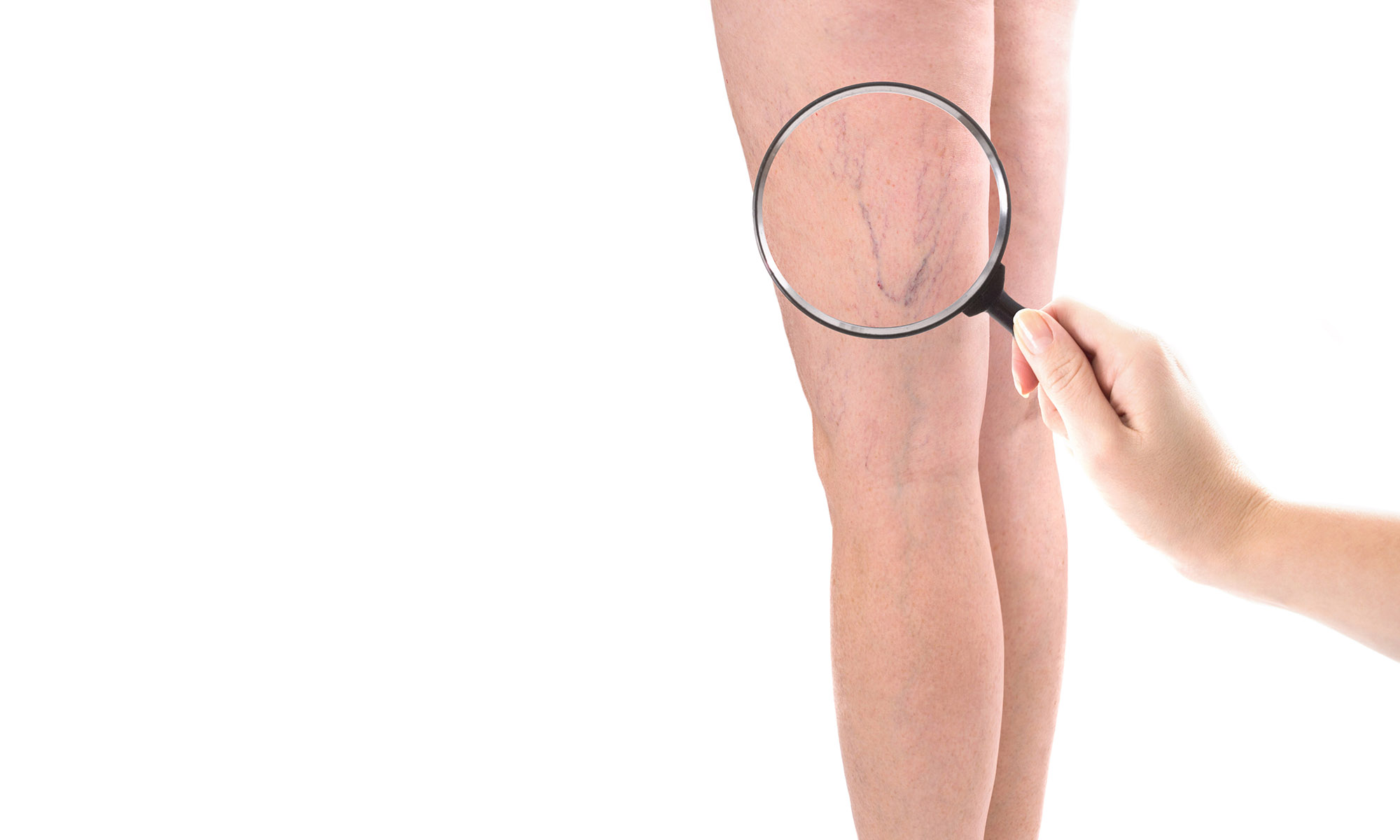
The goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, prevent complications and for some to improve appearance. Lifestyle changes can ease the symptoms, but do not cause the veins to vanish. These treatments include:
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time: To keep blood moving when you have to sit or stand for long periods, try these tips: at work, take walking breaks and try walking during your lunch hour. While sitting, try flexing your feet up and down ten times an hour.
- Exercise: Exercising is good for your veins because it improves blood flow. Walking, cycling or swimming are great exercises for vein health. But be sure to check with your doctor before starting any exercise program.
- Weight loss or maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight puts extra pressure on your veins.
- Leg elevation: Use leg elevation three or four times a day for about 15 minutes at a time. Even elevating your legs on a step stool or ottoman is beneficial. If you need to sit or stand for a long period of time, flexing (bending) your legs occasionally can help keep blood circulating. If you have mild to moderate varicose veins, elevating your legs can help reduce leg swelling and relieve other symptoms.
- Compression stockings: These elastic stockings squeeze or compress the veins and prevent blood from flowing backward. Compression stockings must be graduated, medical-grade compression to be beneficial. Over the counter, support hose or TED hose are not adequate to reduce symptoms in venous disease for active patients.
- Supplements such as horse chestnut and grape seed extract can help reduce symptoms of venous disease. Check with your doctor before starting supplements.
- Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen.
- Anti-inflammatory topical agents such as OTC Arnica, or prescription voltaren gel may be helpful for painful phlebitis.
- Ice packs can be applied to veins that are tender to reduce inflammation
Step 1: The Underlying Problem
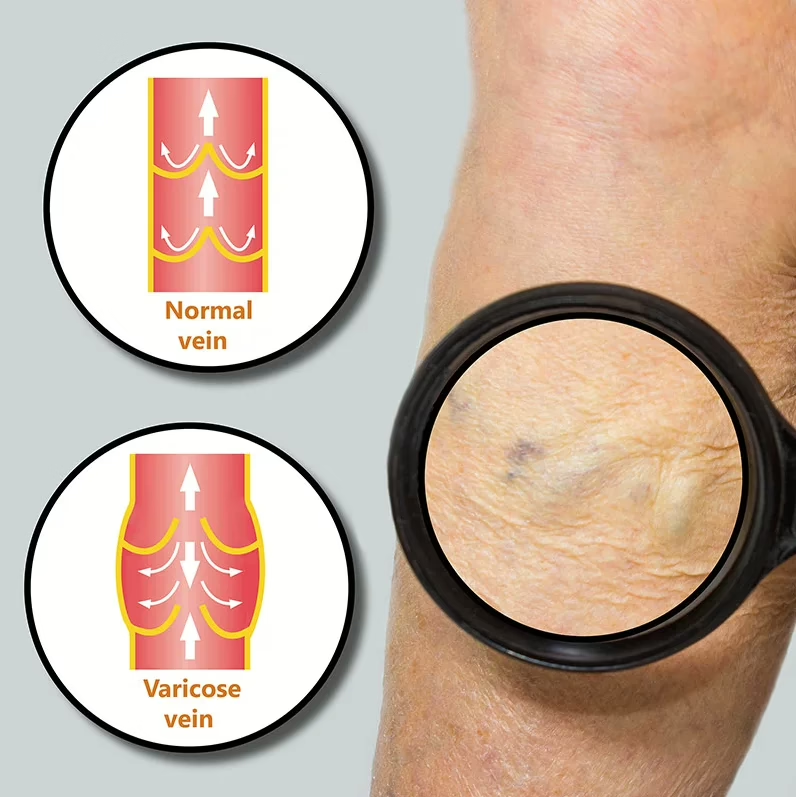
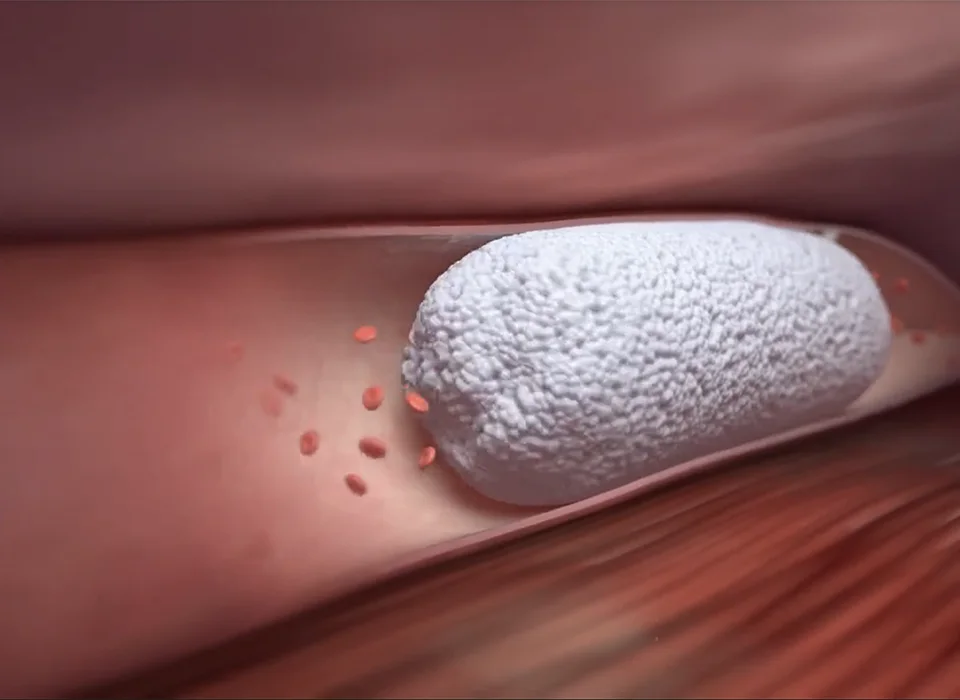
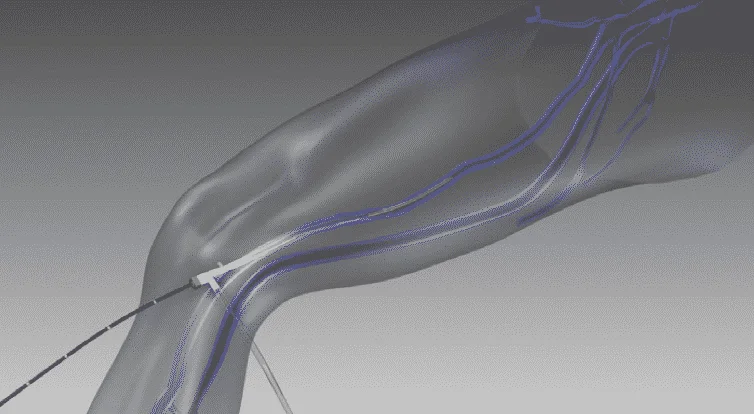
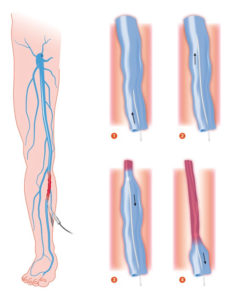
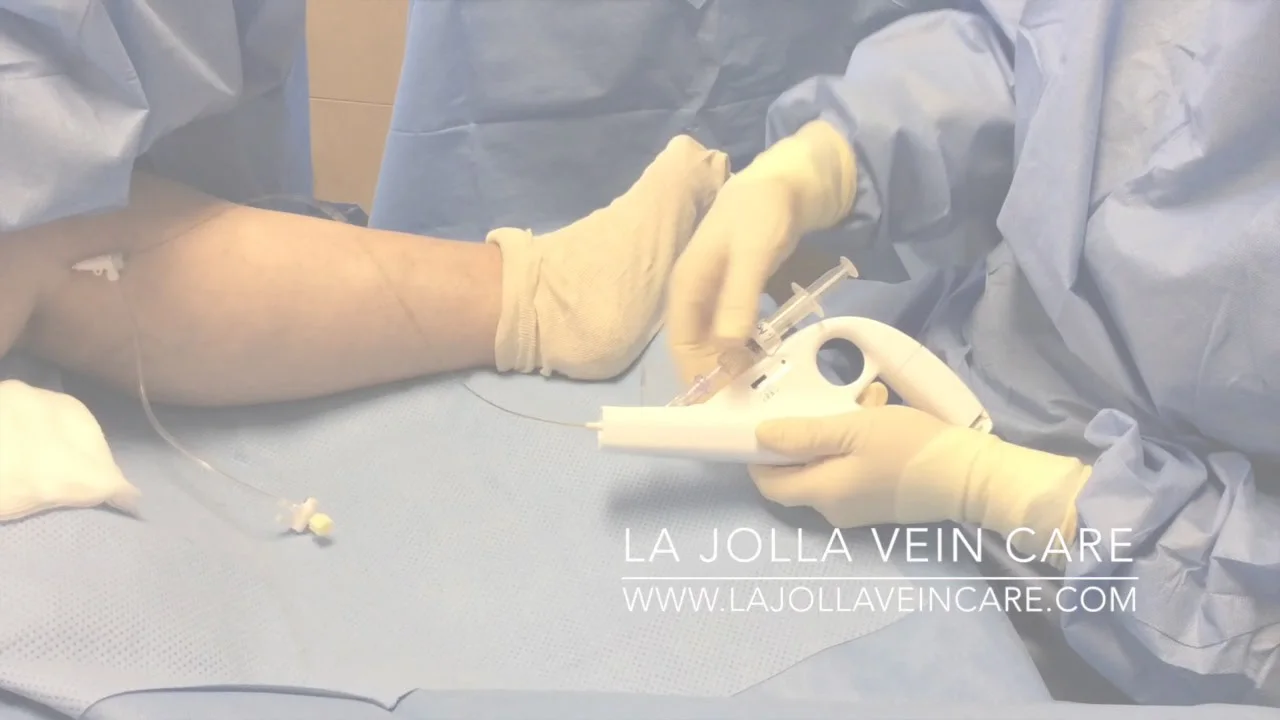
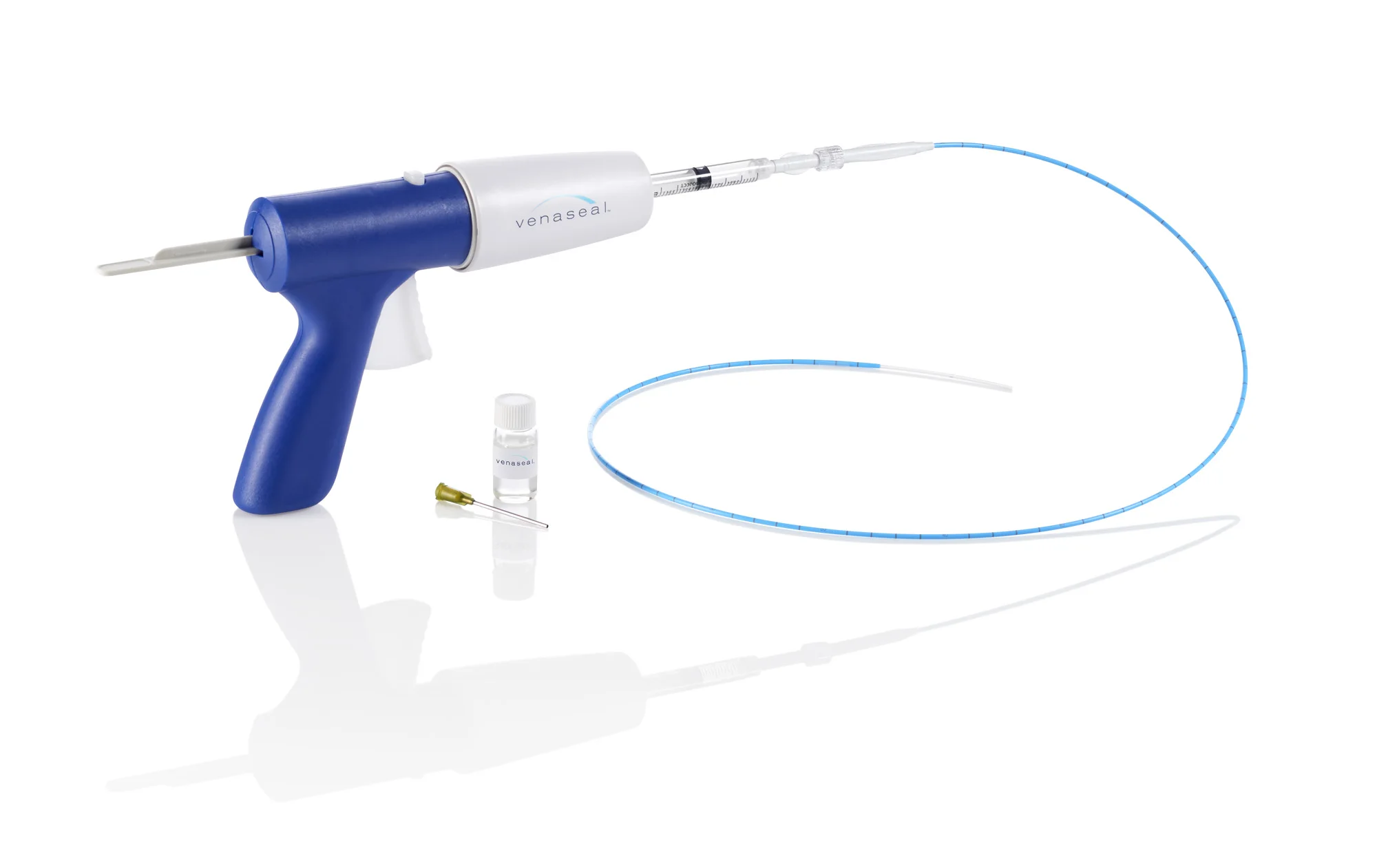
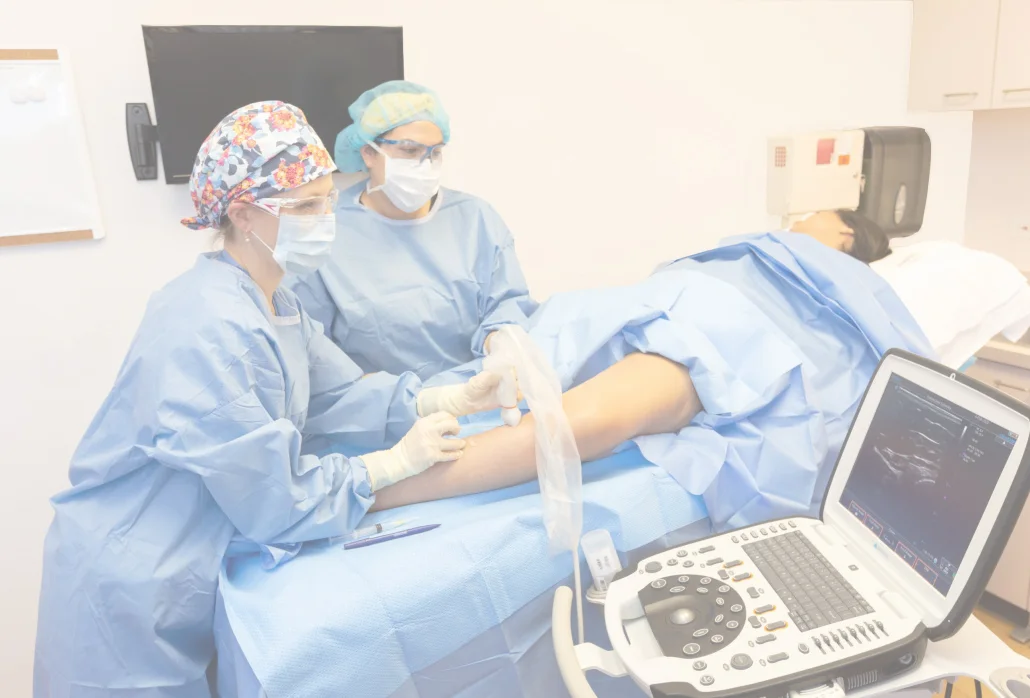
The first step is to treat the underlying problem, the venous reflux. The specific pattern of venous reflux was detected by ultrasound. Venous reflux usually starts in the saphenous veins. The saphenous veins are most effectively treated with vein ablation procedures. This involves placing a small catheter within the vein and using heat or a solution to produce injury and eventual closure of the vein.
The treatment recommendation is customized, based on where reflux is present and other factors that need to be considered when making this decision.
The most commonly used treatments for the saphenous veins are:
These will involve the following:
Your age, overall health, and medical condition.Extent of the condition.The findings of your venous ultrasound.Your signs and symptoms.Your tolerance of specific medicines, procedures, or therapies.Expectations for the course of the condition.Your opinion or preference.
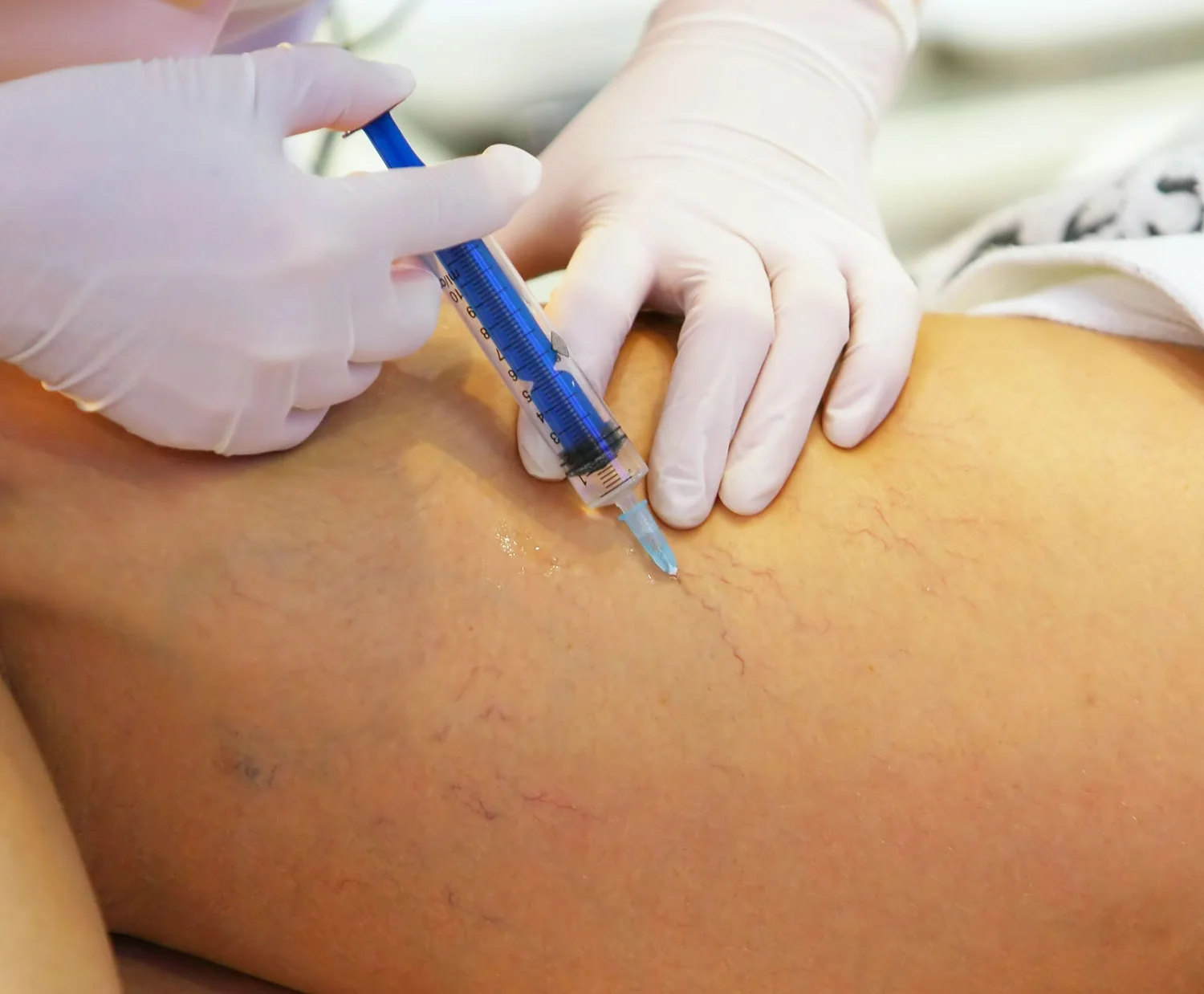
Step 2: Varicose Vein Treatment
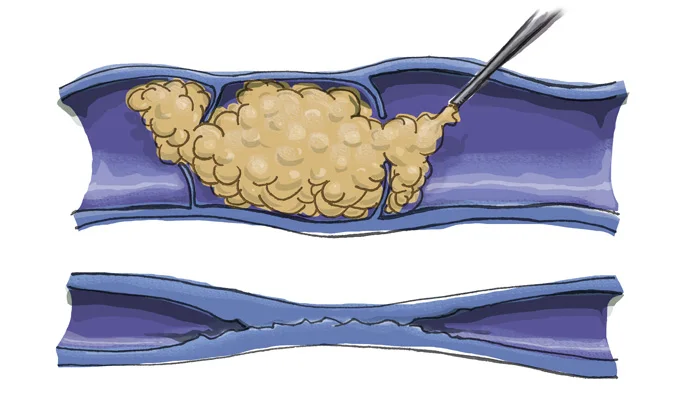
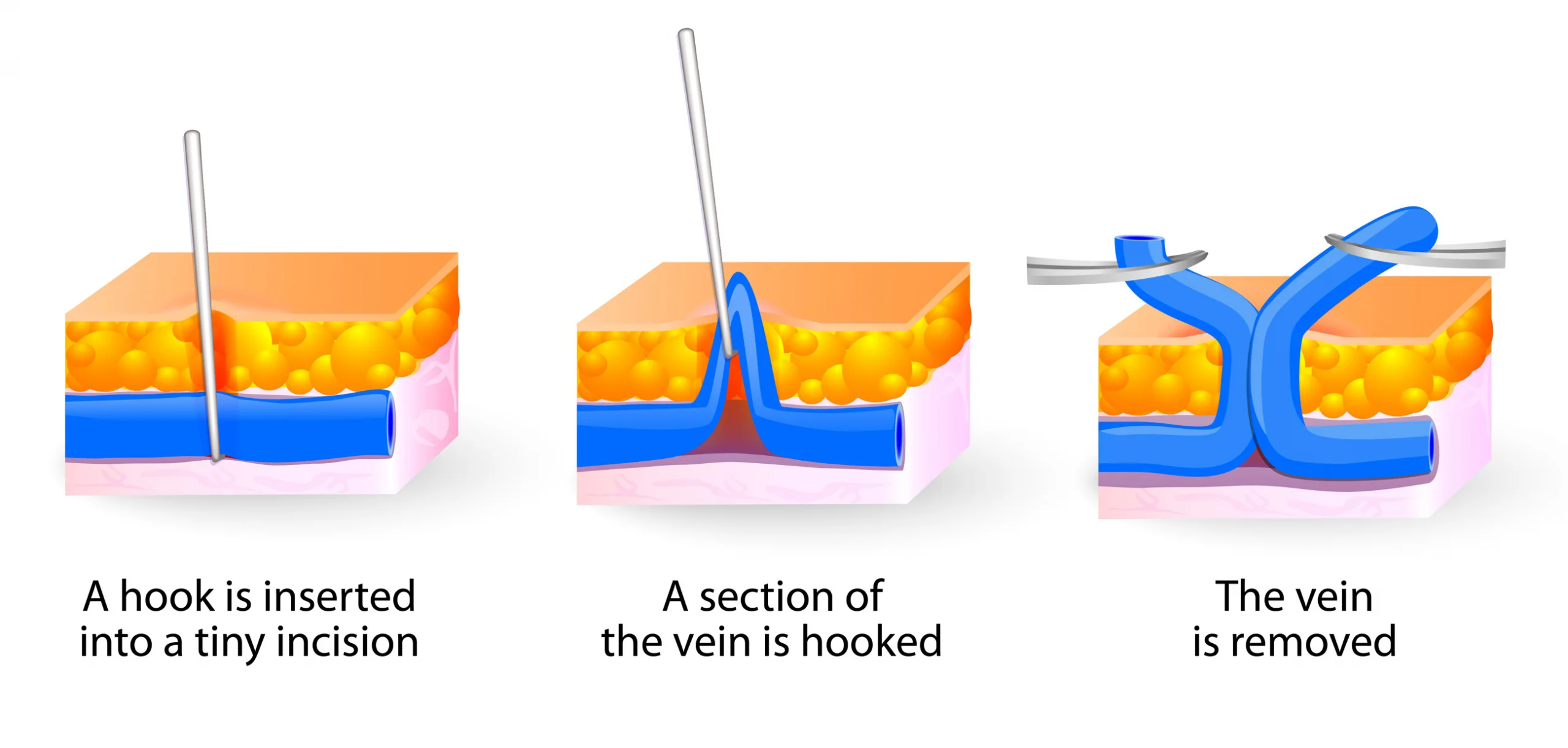
After the underlying saphenous vein reflux is corrected, the bulging veins (varicose veins) can be treated by injecting a foamed medication that will cause them to scar and eventually dissolve (foam sclerotherapy), or to remove them using tiny incisions. The most common method is foam sclerotherapy. This is also known as ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy (UGFS). Phlebectomy is another option which includes making small incisions to remove the vein.